- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
WATER TECHNOLOGY
water is the most useful substance in the nature of the world.the whole living organisms require and utilize the water. without water, no living organism is survived on the nature of the earth. water plays a major role in the nature of the earth.
water is two types;
- according to the depending on the impurities in the water, the water is two types of soft water and hard water.
- hard water is not suitable for many applications.
- hard water needs treatment to use this water for many applications.
read carefully and don't leave any matter until the end.
starts from first;
SOURCE OF WATER:
natural water
1 rainwater(the purest form of water)
2 surface water
3 underground water
4 seawater
Impurities present in the water:
- dissolved and suspended,microscopic impurities.
- dissolved impurities consists of in-organic(mg,k,ca,cl,carbonates,bicarbonates) and organic(humic acid,proteins,amino acid),gases(O2,CO2,N2).
- suspended impurities consists of inorganic(clay,sand),organic(vegetable,animal).
- microscopic impurities consists of bacteria,algae,fungi etc,.
SOFT WATER:
the water which forms lather easily with soap is called soft water.
example:-rainwater.
HARD WATER:
the water which does not form the lather easily with soap is called hard water. example:-seawater.
DEGREE OF HARDNESS:
- degree of hardness means the substances present in water causing the amount of hardness is called the degree of hardness.
- the hardness of water caused by the bicarbonates and sulfates, chlorides of calcium and magnesium present in it.
the hardness of water is two types:
1-temporary hardness:
the temporary hardness of water is due to bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium present in the water. This can be eliminated by the boiling of water.
ex:-calcium carbonate,magnesium carbonate.
2-permanent hardness:
the permanent hardness is due to the chlorides of calcium and magnesium present in it. this hardness does not remove by the boiling of water. this hardness can be removed by the softening of the water processes like the zeolite method and ion exchange method.
ex:-calcium chloride,calcium sulfate,magnesium chloride,magnesium sulfate.
softening of water is nothing but removing hardness from the water is called softening of water.
1 PPM=1 mg/litre=0.1 French units=0.07 clark's
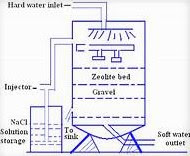
ZEOLITE PROCESS:
- zeolites are also called as permutits.
- zeolite is the process of adding natural or artificial sodium zeolite to the hard water and removes the hardness of the water.
Z=Al2Si2O8.
- the hard water is allowed to pass through the zeolite and it is replaced by the (ca and mg)ions present in water. and soft water is obtained.
- after the completion of zeolite into calcium zeolite and magnesium zeolite and the zeolite can be regenerated by the adding of 10% brine solution it.
- the brine solution is nothing but sodium chloride liquid.
ION EXCHANGE PROCESS:
- ion exchange method is used to remove the hardness of water by the two steps.
- the hard water is allowed to cation exchange resins and the cations are exchanged by the H+ ions.
- the cations are removed and the remaining water is allowed to the anion exchange resins. the chlorides and sulfates and hydro carbonates present in it will be exchanged by the OH- ions of the resin.
- the hardness producing anions are removed.
- the H+, OH- ions are combined to form water. this whole process is known as the ion exchange process.
OSMOSIS:
osmosis is the process of allowing the solution into low concentration to high concentration through a semipermeable membrane.it is a physical process.
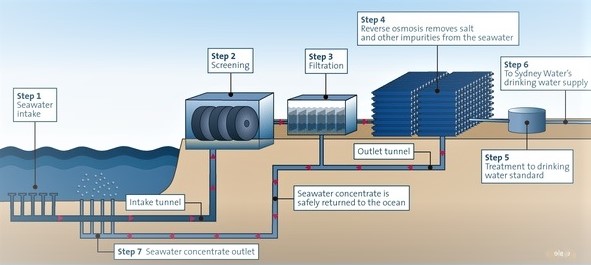
REVERSE OSMOSIS PROCESS:
reverse osmosis is the process of allowing the solution from high concentration to low concentration through a semipermeable membrane, by the osmotic pressure.
NOTE:
about the desalination plant;
Desalination is the process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally,
desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in soil desalination, which is a problem for agriculture. Saltwater is desalinated to produce water suitable for human consumption or irrigation.
the disadvantages of desalination of seawater;
Most desalination plants pump this brine back into the ocean, which presents another environmental drawback. Ocean species aren't equipped to adjust to the immediate change in salinity caused by the discharge of brine into the ocean. The super-saturated saltwater also decreases oxygen levels in the water, causing animals and plants to suffocate.
plants in worldwide;
According to the International Desalination Association, in June 2015, 18,426 desalination plants operated worldwide, producing 86.8 million cubic meters per day, providing water for 300 million people.